| Location | General | Staff and Contact | Data download | Geology an soil |
| Climate | Vegetation | Measurements | Facilities | References |
Location
Degerö Stormyr (64°11′N, 19°33′E, 270 m asl) is located in the Kulbäcksliden Experimental Forest near Vindeln in the county of Västerbotten, Sweden.
The mire covers an area of 6.5 km2 and is situated on a highland between two major rivers, Umeälven and Vindelälven, ca 70 km from the Gulf of Bothnia.
The Degerö ICOS station is located in the Svartberget Experimental Forests and is thus also part of the national infrastructure SITES.
General
The Degerö mire has a long history of scientific research. Scientific investigations started in 1909, and the first PhD thesis "A study of botanical, hydrological and mire development at a mire complex in Northern Sweden" was published by Carl Malmströ in 1923.
More recent research on mire biogeochemistry and biosphere-atmosphere exchange processes started 1995. It is a nutrient poor minerogenic mire, i.e. a fen, representing much of the mire areas in the boreal region.
Degerö is the location of an ICOS Ecosystem station which has been in operation since 2013.
Staff and Contact
Ecosystem station PI: Matthias Peichl
contact: degero@icos-sweden.se
Data download
Final quality controlled ICOS Level2 data from Degerö (SE-Deg) can be downloaded from the ICOS Carbon Portal.
Near real time data (not finally quality controlled) can be accessed through the Carbon Portal: Level 1 data
Pre-ICOS data (2001-2020) can be accessed at the Carbon Portal as Fluxnet Product. These flux data are caluculated by the SPI, while gap-filling and flux separation has been done by the Ecosystem Thematic Center.
Data gathered through the RI SITES: SITES data portal
Geology and Soil
The mire is situated above the highest coastline and thus the area has never been exposed to the sea.
The bedrock constitutes of gneiss, covered with moraines. The Degerö mire consists of a rather complex system of connected smaller mires, divided by islets and ridges of glacial till.
The depth of the peat is generally between 3-4 m, with depths up to 8 m. Organic rich lake sediment started to accumulate about 8000 years ago. Today the deepest peat layers correspond to an age of ~5800 years.
Climate
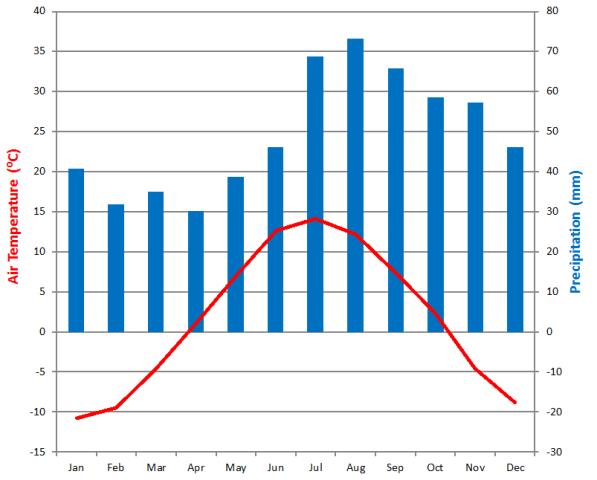
The climate of the site is defined as cold temperate humid (Dfc climate after Köppen) with mean annual precipitation and temperature of 523 mm and +1.2°C respectively, with the mean temperatures in July and January being +14.7°C and -12.4°C, respectively (1961-1990).
Vegetation
The Degerö Stormyr catchment is covered by 69% by mire and 31% by forest: mainly Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) with some Norway spruce (Picea abies). The nutrient poor mineral soils and bedrocks in the region result in nutrient poor conditions which are also clearly reflected by the plant species composition of the mire plant communities.
The area around the measurement mast is dominated by flat mire lawn plant communities with bog mosses (Sphagnum balticum and Sphagnum Lindbergii) dominating the bottom layer. The field layer is dominated by the cottongrass (Eriophorum vaginatum) and the dwraf- shrubs: cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccos L.), bog-rosemary (Andromeda polifolia), deergrass (Trichophorum cespitosum). Sedges (Carex spp.) occur more sparsely.
Average water table depth during the growing season is 10 - 25 cm below the mire surface.
Foliar analyses | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sample type: Andromeda spec.: leaves; Eriophorum vag.: leaves; Sphagnum spec.: until 2020: leaves, thereafter: plant concentration in sample dried at 65°C dry mass ratio: (dry mass at 103 °C) / (dry mass at 65 °C) | ||||||||
| parameter | species | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Ca (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 9.06 | 6.63 | 6.53 | 6.03 | 6.19 | 5.44 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 1.55 | 1.46 | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.28 | 1.51 | 1.54 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 1.53 | 1.64 | 1.64 | 1.29 | 1.70 | 1.53 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 2.54 | 2.53 | 1.70 | 1.48 | 1.76 | 2.01 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 2.12 | 1.49 | 1.65 | 1.64 | 1.42 | 1.58 | 1.44 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 1.77 | 1.79 | 1.92 | 1.63 | 1.35 | 1.67 | 1.46 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 2.74 | 2.88 | 2.92 | 2.32 | 3.03 | 3.93 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 2.02 | 2.06 | 2.11 | 2.42 | 2.26 | 2.85 | 3.05 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 1.38 | 5.21 | 1.99 | 1.31 | 1.85 | 2.26 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 2.14 | 3.54 | 2.68 | 2.27 | 2.87 | 3.97 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 0.53 | 1.69 | 4.15 | 2.33 | 1.43 | 1.92 | 2.40 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 1.34 | 1.96 | 2.77 | 2.46 | 2.01 | 2.35 | 2.53 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 23.88 | 27.48 | 27.93 | 19.24 | 27.94 | 22.98 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 63.06 | 43.02 | 106.89 | 52.06 | 55.78 | 55.50 | 53.64 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 841.3 | 6301.5 | 1070.4 | 504.6 | 991.2 | 868.8 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 2183.3 | 2523.3 | 260.0 | 249.1 | 409.6 | 190.6 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 2200.0 | 1239.3 | 7274.5 | 1336.4 | 730.6 | 1242.4 | 1135.8 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 2215.0 | 1595.0 | 1807.5 | 935.0 | 656.6 | 1323.0 | 859.8 | |
| Mg (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 1.768 | 1.41 | 1.55 | 1.49 | 1.54 | 1.53 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.92 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.80 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 1.07 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.87 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.79 | 0.70 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.65 | |
| Mn (mg/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 214.6 | 117.8 | 167.0 | 191.6 | 165.6 | 203.2 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 67.0 | 57.9 | 62.6 | 55.5 | 56.2 | 64.9 | 74.8 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 63.7 | 51.1 | 33.7 | 42.5 | 36.14 | 34.58 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 75.7 | 121.2 | 165.8 | 155.2 | 145.6 | 278.0 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 30.8 | 51.7 | 55.2 | 32.3 | 39.4 | 32.4 | 31.4 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 35.3 | 58.5 | 62.4 | 84.8 | 56.0 | 50.3 | 66.7 | |
| C (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 531.6 | 526.5 | 532.5 | 529.0 | 530.0 | 530.4 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 487.4 | 492.8 | 488.0 | 494.2 | 494.8 | 492.0 | 494.2 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 468.3 | 471.0 | 473.6 | 473.8 | 470.8 | 475.2 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 484.3 | 478.7 | 484.6 | 483.8 | 483.2 | 484.6 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 468.5 | 475.3 | 469.3 | 477.0 | 480.4 | 476.8 | 480.4 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 479.3 | 480.8 | 478.8 | 481.4 | 486.4 | 482.6 | 486.0 | |
| N (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 13.18 | 11.18 | 12.08 | 11.04 | 11.56 | 10.62 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 14.41 | 15.81 | 16.28 | 16.54 | 16.72 | 17.86 | 16.56 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 6.29 | 6.53 | 6.51 | 5.56 | 6.0 | 6.09 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 5.91 | 6.55 | 6.72 | 7.60 | 6.76 | 7.75 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 5.98 | 6.92 | 7.27 | 7.40 | 6.19 | 6.64 | 6.32 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 5.45 | 6.00 | 6.30 | 7.90 | 6.91 | 5.69 | 5.44 | |
| P (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.95 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.30 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.46 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.29 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.28 | |
| K (g/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 4.29 | 4.62 | 5.06 | 4.79 | 5.18 | 5.08 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 5.93 | 6.20 | 6.31 | 6.07 | 6.33 | 6.13 | 5.71 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 4.57 | 4.62 | 4.65 | 4.98 | 5.23 | 4.95 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 3.46 | 4.29 | 3.67 | 5.65 | 4.45 | 5.75 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 3.95 | 4.01 | 4.80 | 4.88 | 4.89 | 5.23 | 4.90 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 3.71 | 3.36 | 4.12 | 4.20 | 4.73 | 4.29 | 4.14 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 36.68 | 30.35 | 30.53 | 24.74 | 30.18 | 28.5 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 54.68 | 51.92 | 54.26 | 43.16 | 42.32 | 61.28 | 66.8 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 37.88 | 132.85 | 31.82 | 24.88 | 37.74 | 37.9 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 48.47 | 71.13 | 30.56 | 27.3 | 37.6 | 36.4 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 34.5 | 33.6 | 30.15 | 29.61 | 22.06 | 33.6 | 29.9 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 33.85 | 41.65 | 54.13 | 28.10 | 19.42 | 28.86 | 38.3 | |
| dry mass ratio (%) | Andromeda polifolia L. | -- | 91.42 | 91.73 | 93.9 | 91.62 | 91.98 | 91.08 |
| Eriophorum vaginafum L. | 93.35 | 91.81 | 90.55 | 93.22 | 89.98 | 90.92 | 90.84 | |
| Sphagnum balticum | -- | 88.73 | 86.83 | 89.10 | 84.18 | 87.06 | 84.32 | |
| Sphagnum fuscum | -- | 87.17 | 86.43 | 88.90 | 84.42 | 87.12 | 83.22 | |
| Sphagnum lindbergii | 89.95 | 88.18 | 86.90 | 88.82 | 82.14 | 87.16 | 83.2 | |
| Sphagnum papillosum | 90.87 | 87.70 | 86.50 | 88.64 | 84.76 | 87.36 | 83.5 | |
Measurements
Measured Ecosystem station variables and summary of station parameters
Variables and measurement heights included in the Ecosystem station program at Degerö are listed on the Ecosystem station introduction page: follow this link to the page
Non-ICOS measurements
The ICOS station Degerö is located in the Krycklan catchment area, which is part of SITES. It also hosts other complementary measurements from various research projects.
Several long-term, still ongoing, field manipulation experiments as well as shorter research projects are carried out within the mire catchment. The research at the site covers a large variety of general ecological and biogeochemical research questions with some focus on carbon biogeochemistry of methane production, oxidation, and emission.
Continuous measurements of the biosphere-atmosphere exchange of CO2 by eddy covariance started 2001. Since more than ten years all significant carbon fluxes (biosphere-atmosphere flux of carbon dioxide CO2 and methane CH4 as well as the discharge export of both organic and inorganic carbon) are covered.
For more detailed information please contact the station.
References
Please, see the list at the SLU's webpage: selected publications with data from Degerö
ICOS ETC labelling report:




